•Class 3 malocclusion is a type of dental misalignment where the lower teeth and jaw protrude forward in relation to the upper teeth and jaw. This type of malocclusion is also known as prognathism, underbite, or negative overjet. •Class 3 malocclusion can be further classified into two subtypes: •True Class 3: In this subtype, the lower jaw is significantly protruded forward, causing the lower teeth to overlap or come in front of the upper teeth. The upper front teeth may also be retruded or sit behind the lower front teeth. •Pseudo Class 3: In this subtype, the lower teeth are in a normal position, but the upper teeth are retruded, giving the appearance of an underbite. •Class 3 malocclusion can cause various issues, such as difficulty in biting and chewing, speech problems, and aesthetic concerns. Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, can help correct Class 3 malocclusion and improve dental function and appearance. In some cases, additional treatments, such as jaw surgery, may be necessary to correct severe cases of Class 3 malocclusion. It’s important to consult with a dental professional if you suspect you have a malocclusion or other dental issue. •
Qu’est ce qu’une malocclusion de classe 2 ?
•La malocclusion de Classe 2 est un type de mauvaise alignement dentaire où les dents et la mâchoire supérieure sont projetées vers l’avant par rapport aux dents et à la mâchoire inférieures. Ce type de malocclusion est également appelé rétrognathisme, surplomb ou surplomb horizontal excessif. •La malocclusion de Classe 2 peut être classée en deux sous-types : •Division 1 : Dans ce sous-type, les dents supérieures avant sont nettement projetées vers l’avant et dépassent souvent les dents inférieures avant, créant un surplomb sévère. •Division 2 : Dans ce sous-type, les dents supérieures avant sont inclinées vers l’arrière et la mâchoire supérieure est toujours projetée vers l’avant, mais pas aussi gravement que dans la Division 1. Il peut également y avoir une surplomb vertical excessif, où les dents supérieures avant recouvrent une partie importante des dents inférieures avant. •La malocclusion de Classe 2 peut causer divers problèmes, tels que des difficultés à mordre et à mâcher, des problèmes d’élocution, un risque accru de traumatisme dentaire et des préoccupations esthétiques. Le traitement orthodontique, tel que les appareils dentaires ou les aligneurs transparents, peut aider à corriger la malocclusion de Classe 2 et à améliorer la fonction et l’apparence dentaires. Dans certains cas, des traitements supplémentaires, tels que la chirurgie maxillo-faciale, peuvent être nécessaires pour corriger les cas graves de malocclusion de Classe 2. Il est important de consulter un professionnel de la santé dentaire si vous soupçonnez une malocclusion ou un autre problème dentaire. •
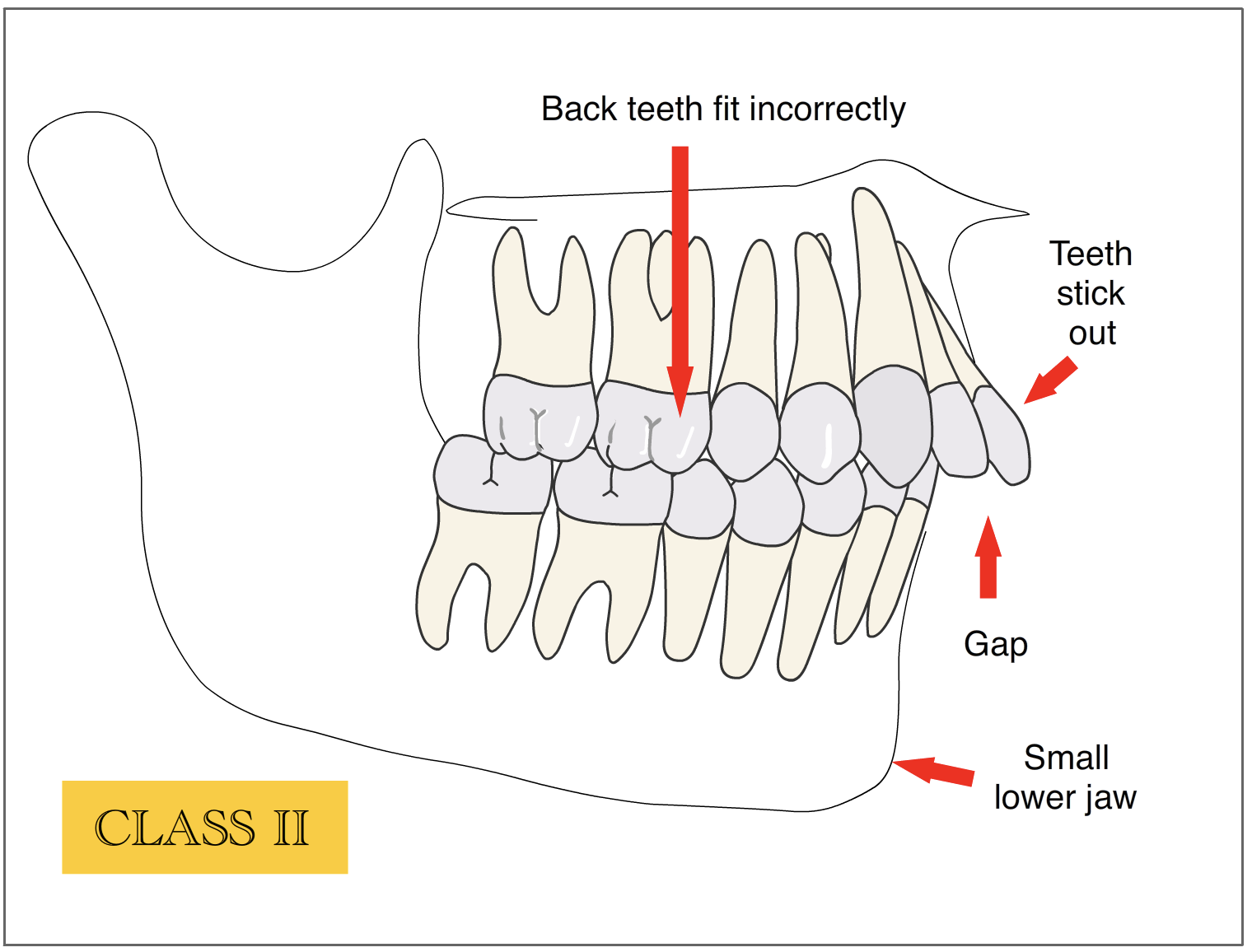
What is class 2 malocclusion?
•Class 2 malocclusion is a type of dental misalignment where the upper teeth and jaw protrude forward in relation to the lower teeth and jaw. This type of malocclusion is also known as retrognathism, overbite, or overjet. •Class 2 malocclusion can be further classified into two subtypes: •Division 1: In this subtype, the upper front teeth are significantly protruded forward and often stick out over the lower front teeth, creating a severe overbite. •Division 2: In this subtype, the upper front teeth are tipped backward, and the upper jaw is still protruded, but not as severely as in Division 1. There may also be a deep bite, where the upper front teeth cover a significant portion of the lower front teeth. •Class 2 malocclusion can cause various issues, such as difficulty in biting and chewing, speech problems, increased risk of dental trauma, and aesthetic concerns. Orthodontic treatment, such as braces or clear aligners, can help correct Class 2 malocclusion and improve dental function and appearance. In some cases, additional treatments, such as jaw surgery, may be necessary to correct severe cases of Class 2 malocclusion. It’s important to consult with a dental professional if you suspect you have a malocclusion or other dental issue. •
Quels sont les différences entre un traitement avec des coquilles en plastiques et les appareils en boitier de métal conventionnel?
•L’orthodontie avec des brackets et les aligneurs sont deux options de traitement orthodontique visant à redresser les dents et à améliorer leur alignement. Cependant, il existe des différences importantes entre ces deux options. •Les brackets, également connus sous le nom de boitiers, sont un traitement orthodontique traditionnel qui consiste à fixer des brackets métalliques ou en céramique sur les dents, qui sont ensuite reliés par un fil. Le fil est serré au fil du temps, ce qui exerce une pression douce sur les dents, les déplaçant progressivement vers la position souhaitée. Les brackets sont un appareil fixe, ce qui signifie qu’ils ne peuvent pas être enlevés par le patient. •D’autre part, les aligneurs sont un traitement orthodontique plus récent qui implique le port d’une série de gouttières en plastique transparentes et amovibles qui sont fabriquées sur mesure pour s’adapter aux dents. Chaque gouttière est portée pendant une période de temps avant d’être remplacée par la suivante de la série, déplaçant progressivement les dents vers la position souhaitée. Les aligneurs sont un appareil amovible, ce qui signifie qu’ils peuvent être retirés pour manger, se brosser les dents et passer du fil dentaire. •Certaines des principales différences entre les brackets et les aligneurs comprennent : •Apparence : Les brackets sont faits de brackets métalliques ou en céramique et de fils, qui sont visibles sur les dents. Les aligneurs sont faits de plastique transparent, ce qui les rend beaucoup moins perceptibles. •Confort : Les brackets peuvent causer de l’inconfort ou de la douleur, en particulier au cours des premiers jours ou après les ajustements. Les aligneurs sont généralement plus confortables, bien que certaines personnes puissent ressentir une légère gêne ou une pression initiale lorsqu’elles commencent à porter une nouvelle gouttière. •Entretien : Les brackets nécessitent des soins supplémentaires pour les maintenir propres, car des particules alimentaires peuvent se coincer dans les brackets et les fils. Les aligneurs doivent être enlevés pour manger et boire, et doivent être nettoyés quotidiennement pour éviter les taches et les odeurs. •Durée du traitement : Les brackets prennent généralement plus de temps que les aligneurs pour redresser les dents. Cependant, la durée du traitement peut varier en fonction du cas individuel. •Coût : Le coût des brackets et des aligneurs peut varier en fonction du plan de traitement spécifique et du prestataire. Dans l’ensemble, les brackets et les aligneurs peuvent être efficaces pour traiter les problèmes orthodontiques, et le choix entre les deux options dépendra des besoins et des préférences de chaque personne. Votre orthodontiste peut vous aider à déterminer quelle option est la meilleure pour vous.
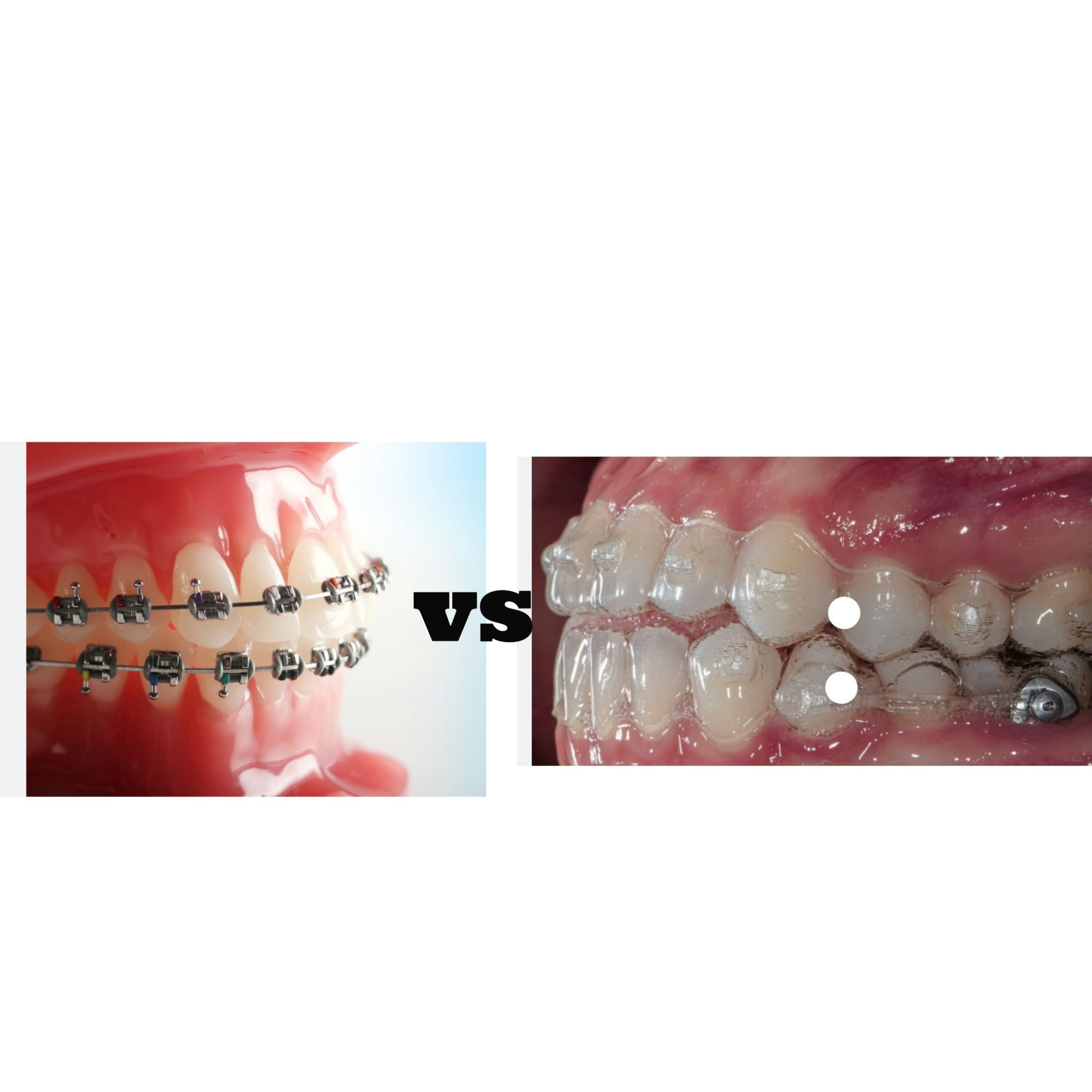
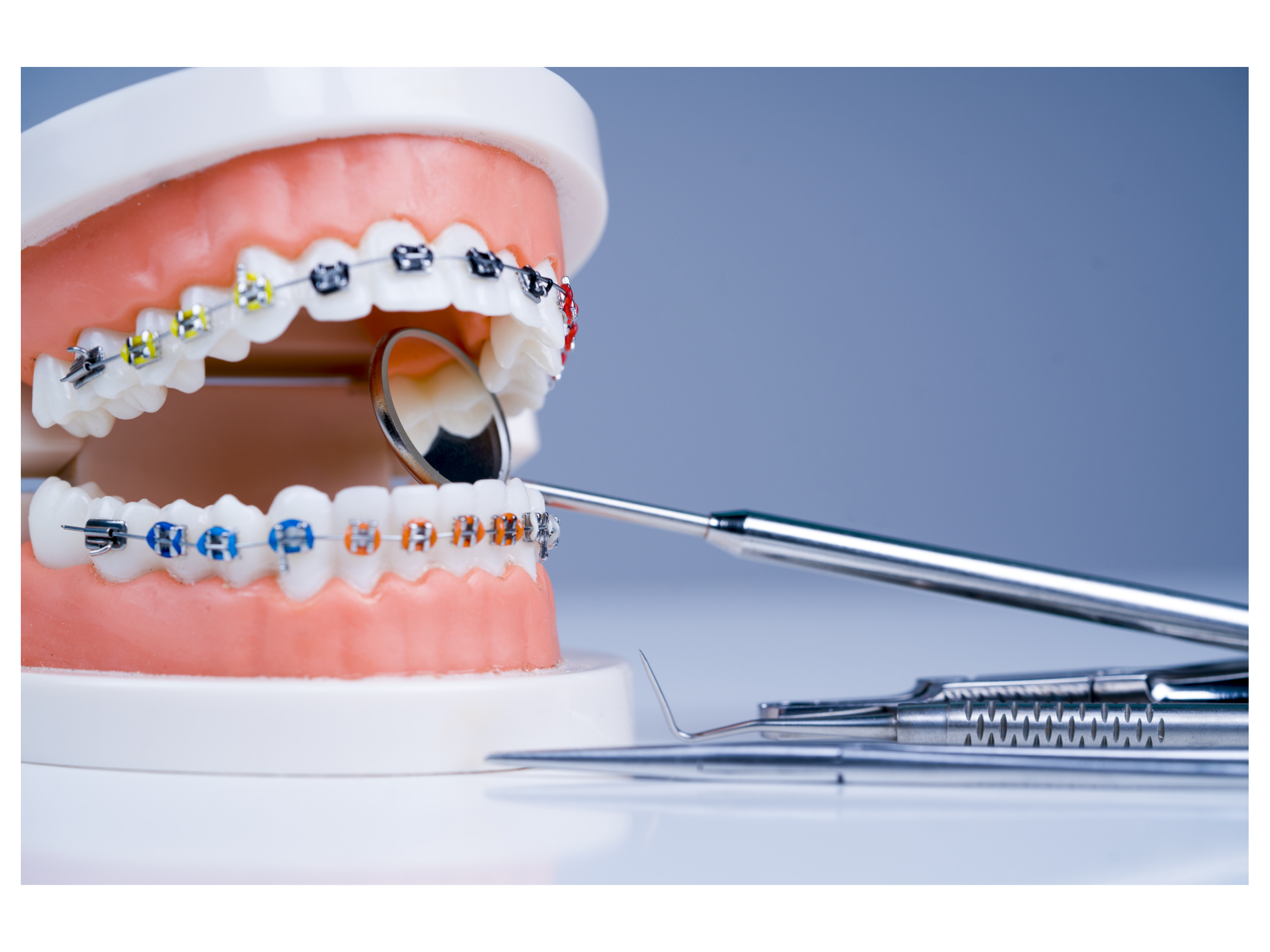
What are the differences between a treatment with clear aligners vs conventional braces ?
•Orthodontics with brackets and aligners are both orthodontic treatment options that aim to straighten teeth and improve their alignment. However, there are some important differences between the two options. •Braces, which are also known as brackets, are a traditional orthodontic treatment that involve attaching metal or ceramic brackets to the teeth, which are then connected by a wire. The wire is tightened over time, which applies gentle pressure to the teeth, gradually moving them into the desired position. Braces are a fixed appliance, which means they cannot be removed by the patient. •On the other hand, aligners are a newer orthodontic treatment that involves wearing a series of clear, removable plastic trays that are custom-made to fit over the teeth. Each tray is worn for a period of time before being replaced by the next tray in the series, gradually moving the teeth into the desired position. Aligners are a removable appliance, which means that they can be taken out for eating, brushing and flossing. •Some of the key differences between brackets and aligners include: •Appearance: Braces are made of metal or ceramic brackets and wires, which are visible on the teeth. Aligners are made of clear plastic, which makes them much less noticeable. •Comfort: Braces can cause discomfort or soreness, particularly in the first few days or after adjustments. Aligners are generally more comfortable, although some people may experience some initial discomfort or pressure when they start wearing a new tray. •Maintenance: Braces require extra care to keep them clean, as food particles can get trapped in the brackets and wires. Aligners need to be removed for eating and drinking, and they need to be cleaned daily to avoid staining and odor. •Treatment Time: Braces typically take longer to straighten teeth than aligners. However, the length of treatment time can vary depending on the individual case. •Cost: The cost of braces and aligners can vary depending on the specific treatment plan and the provider. Overall, both braces and aligners can be effective in treating orthodontic issues, and the choice between the two options will depend on the individual’s specific needs and preferences. Your orthodontist can help you to determine which option is best for you.
Quels sont les bénéfices d’un traitement orthodontique?
•Le traitement d’orthodontie peut offrir de nombreux avantages, notamment : ·Un meilleur alignement dentaire pour une apparence plus esthétique ·Une amélioration de la fonction dentaire, y compris la mastication et la parole ·Une réduction du risque de caries dentaires et de maladies des gencives ·Une réduction du risque de traumatisme dentaire ·Un alignement correct des mâchoires pour réduire les problèmes de l’articulation temporo-mandibulaire ·Une amélioration de la confiance en soi grâce à une meilleure apparence dentaire. ·Il est important de consulter un professionnel de la santé dentaire pour déterminer si un traitement d’orthodontie est approprié pour vos besoins dentaires individuels. •
What are the benefits of an orthodontic treatment ?
•Orthodontic treatment has many benefits, including: •Improved Oral Health: Orthodontic treatment helps align teeth, reducing the risk of gum disease, tooth decay, and abnormal wear of the tooth surfaces. Proper alignment also makes it easier to clean teeth, which can help prevent future oral health problems. •Enhanced Appearance: Straight teeth improve the overall appearance of a smile, boosting self-confidence and self-esteem. Orthodontic treatment can help correct overcrowding, gaps, and misaligned teeth, resulting in a more attractive smile. •Improved Function: Orthodontic treatment can help correct bite issues, such as overbites, underbites, and crossbites. Proper bite alignment can improve chewing and speech abilities, as well as prevent jaw pain and discomfort. •Reduced Risk of Injury: Protruding teeth are more susceptible to injury during sports or accidents. Orthodontic treatment can help align teeth, reducing the risk of injury and damage to the teeth. •Long-Term Savings: While orthodontic treatment can be a significant investment, it can ultimately save money in the long run by preventing more expensive dental procedures and addressing oral health issues before they become more severe. •Overall, orthodontic treatment can improve oral health, enhance appearance, improve function, reduce the risk of injury, and potentially save money in the long run. •